褐藻是海洋大型藻类中规模最大、形态最复杂的一类,褐藻胶(Alginate)是褐藻的基本碳水化合物成分[1]。褐藻纲中,尤其是在曾藻目和岩藻目中, 一些海藻所含的褐藻胶量特别大,约占其干质量的55%[2]。褐藻胶是一种线性多糖,由β-D-甘露糖醛酸(β-D-mannuronate,M)以及α-L-古罗糖醛酸(α-L-guluronate,G)构成,这2种差向异构体可以形成3种不同的嵌段(多聚甘露糖醛酸片段(polyM)、多聚古罗糖醛酸片段(polyG)以及交替杂合片段(polyMG))[3]。褐藻胶具有优异的凝胶性、稳定性以及增稠性,在食品、纺织、医药等领域有着广泛的应用[4]。但是褐藻胶分子量大,难以被机体吸收利用,限制了其应用的广泛程度。由于褐藻胶制备形成的褐藻寡糖(Alginate oligosaccharides,AOS)具有比褐藻胶分子量小、水溶性高以及黏度低的优势,因此褐藻寡糖的应用范围更广[5]。褐藻寡糖具有抗氧化、抗菌、抗糖尿病、抗高血压、抗肿瘤、抗凝血、免疫调节以及促进植物生长等活性[6-8]。
研究表明,同物理法以及化学法相比,酶解法(所用的酶主要是褐藻胶裂解酶)制备褐藻寡糖具有作用条件温和、产率高的优势,在褐藻寡糖产业化制备中具有重要的应用前景[9]。褐藻胶裂解酶(Alginate lyases)属于多糖裂解酶家族(Polysaccharide lyases family,PL),主要是通过β-消除反应降解褐藻胶[10]。在碳水化合物酶的数据库中(http://www.cazy.org/),根据一级序列,已发现的褐藻胶裂解酶被分成14个褐藻胶裂解酶家族,分别是PL5、PL6、PL7、PL8、PL14、PL15、PL17、PL18、PL31、PL32、PL34、PL36、PL39以及PL41[11]。越来越多的褐藻胶裂解酶被表征,但由于以往的褐藻胶裂解酶存在纯化繁琐、稳定性差以及酶活力低等问题,导致其极少应用于生产制备褐藻寡糖[12]。因此,仍需要不断开发挖掘新型的褐藻胶裂解酶,应用于褐藻寡糖的大规模制备[13-14]。
本文从颊吻鼻鱼肠道酶筛选到一株海洋细菌Pseudoalteromonas sp. 01,从中克隆了一个PL7家族的褐藻胶裂解酶,该酶是双功能的内切酶,能够有效降解各种形式的褐藻胶,产生聚合度(Degrees of polymerization,DPs)为2~4的褐藻寡糖。酶学性质表明,该酶能够在适中的反应温度以及较宽的pH范围发挥作用,具有开发成为工具酶的潜能。
1 仪器,材料与方法 1.1 菌株、试剂与仪器菌株:E. coli BL21(DE3)、质粒pET32a-p以及Prescission蛋白酶均由本实验室制备并保存;Pseudoalteromonas sp. 01是从颊吻鼻鱼肠道微生物中获得,并由实验室保存。
试剂:褐藻胶购自上海源叶生物有限公司;通过酸解法制备而获得polyM和polyG[15];Ni-NTA琼脂糖凝胶购自于康为世纪生物科技有限公司;所使用的限制性内切酶是BamH Ⅰ和Xho Ⅰ,所使用的T4 DNA连接酶以及PrimerSTAR® HS DNA聚合酶均购自于Omega Bio-Tek公司;其他化学试剂均购自于国药集团。
仪器:T100 PCR仪(供应商:美国Bio-RAD);电泳仪(供应商:北京六一仪器厂);垂直蛋白电泳装置(供应商:美国BIO-RAD);细胞超声破碎仪(供应商:宁波新芝生物科技有限公司);酶标仪(供应商:美国Bio-Tek)。
1.2 实验方法 1.2.1 AlyPC1序列分析基于微生物培养法,从颊吻鼻鱼肠道微生物中筛选到一株高效降解褐藻胶的菌株Pseudoalteromonas sp. 01,推测其基因组中含有降解褐藻胶的相关酶系。对其基因组进行测序,从注释的信息中获得了一个褐藻胶裂解酶的基因,将该酶命名为AlyPC1。
首先,使用在线软件SignalP 5.0(http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/SignalP/)预测AlyPC1的信号肽,使用在线软件SMART(http://smart.embl.de)[16]预测分析AlyPC1的结构域, 利用MEGA 7.0中最大拟然法, 将AlyPC1的氨基酸序列同PL7家族各成员的氨基酸序列进行比对分析,构建系统发育树。利用Bioedit软件对AlyPC1和同亚家族的序列进行多序列比对,然后利用在线软件ESPript 3.0 (http://espript.ibcp.fr/ESPript/ESPript/index.php)对多序列比对结果进行分析。通过在线软件Protparam(https://web.expasy.org/protparam/)预测AlyPC1的分子量。
1.2.2 AlyPC1原核表达载体的构建以Pseudoalteromonas sp. 01基因组DNA为模板,设计PCR正向引物PC1-F(CGCGGATCCTGTGGCTCATCATCACCAACTAATG)和反向引物PC1-R(CCGCTCG-AGTTAATTATGTGAAGTAAATAAGCGATAG),获得了不含信号肽的alypc1片段。引物PC1-F和PC1-R分别含有BamHⅠ的酶切位点和 XhoⅠ的酶切位点,利用限制性内切酶BamHⅠ和 XhoⅠ将PCR片段酶切;同时利用上述限制性内切酶将质粒pET32a-p线性化。将酶切片段与质粒pET32a-p通过T4 DNA连接酶连接;连接产物转化入E.coli BL21(DE3)中,获得的阳性克隆,送至上海生工生物有限公司进行测序,并将其中测序正确的克隆被命名为pET32a-AlyPC1。
将保存的甘油菌pET32a-AlyPC1按照1%的比例接种于含有氨苄霉素(Amp)抗性的50 mL溶菌肉汤(LB)液体培养基中,在37 ℃条件下180 r/min摇床培养12 h;活化的菌株按照1%的接种量接种于含有1 L LB液体培养基的锥形瓶中,培养基中加入Amp,在37 ℃条件下培养,待OD600值在0.6~0.8之间时,向培养基中加入终浓度为0.1 mmol/L的异丙基-β-D-硫代半乳糖苷(IPTG),16 ℃ 180 r/min培养20 h。
培养结束后收集菌体,然后使用15 mL的缓冲液(Tris-HCl(pH=7.5)20 mmol/L、NaCl 500 mmol/L和咪唑10 mmol/L)重悬菌体,使用超声破碎仪破碎菌体(程序为超声2 s后暂停4 s,总循环时间为25 min);超声破碎结束后,12 000g离心30 min,收集上清液。上清液通过镍离子金属鳌合亲和层析介质(Ni-NTA)琼脂糖凝胶亲和层析纯化后,用蛋白酶酶切,以除去融合蛋白中硫氧还蛋白(TRX)标签,获得目的蛋白AlyPC1。用十二烷基硫酸钠聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳(Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, SDS-PAGE)分析蛋白纯度,使用酶标仪检测OD280值,测定蛋白浓度。
1.2.3 酶活力性测定将褐藻胶底物溶解于含Tris-HCl(pH=8.0)20 mmol/L + NaCl 200 mmol/L的缓冲液中,配制成浓度为2 mg/mL褐藻胶溶液。反应体系有200 μL,其中包括190 μL底物溶液(2 mg/mL)以及10 μL 0.06 mg/mL的AlyPC1,在35 ℃条件下反应5 min,反应结束后在100 ℃灭活10 min。由于降解产生的褐藻寡糖含有不饱和双键,在波长235 nm处有高吸收值,因此,取200 μL反应产物检测OD235值。以190 μL褐藻胶以及10 μL的缓冲液(Tris-HCl(pH=8.0)20 mmol/L + NaCl 200 mmol/L)的反应作为对照组。酶活力单位(U)定义为每分钟OD235增加1为1 U[17]。
1.2.4 AlyPC1酶学性质表征为确定AlyPC1的最适反应温度,在5~60 ℃下进行酶活测定;为测定热稳定性,将酶在5~60 ℃条件下孵育1 h后,测定其剩余活性。为了研究AlyPC1的最适反应pH,将底物溶解于浓度为20 mmol/L的不同pH的缓冲液中,其中缓冲液有CH3COONa溶液(pH在5.0~6.0之间)、Na2HPO4-NaH2PO4溶液(pH在6.0~7.5之间)、Tris-HCl溶液(pH在7.5~9.0之间)和Gly-NaOH溶液(pH在9.0~11.0之间)4种,并在最适反应温度下测定酶活。为了确定NaCl含量对AlyPC1酶活性的影响,向反应底物中添加不同比例的NaCl,NaCl含量梯度设定为0、50、100、200、300、400、500和600 mmol/L。为测定不同金属离子和EDTA对AlyPC1的影响,将反应体系分成10组,每组中分别添加1 mmol/L的K+、Na+、Cu2+、Co2+、Ca2+、Mg2+、Zn2+、Ni2+、Mn2+和EDTA,以不添加任何金属离子测定的酶活性为对照,测定AlyPC1的酶活。为测定底物专一性,将褐藻胶、polyG和polyM作为底物,分别溶解于三个20 mmol/L Tris-HCl(pH=8.0)+200 mmol/L NaCl缓冲液中,在最适反应条件下测定酶的底物专一性。
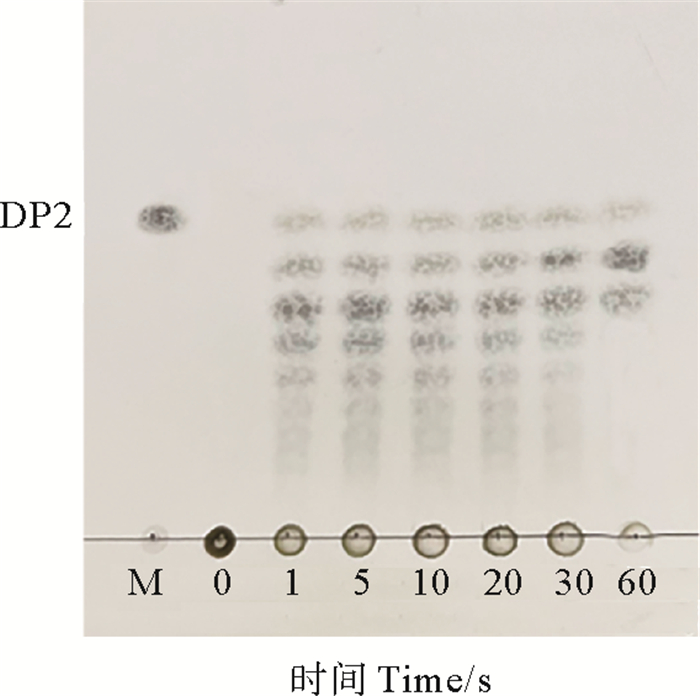
1.2.5 AlyPC1对褐藻胶的降解过程将2 mg/mL褐藻胶溶解于20 mmol/L Tris-HCl(pH=8.0)+200 mmol/L NaCl缓冲液中,取100 μL褐藻胶同3 U的AlyPC1反应,分别在降解0、1、5、10、20、30和60 min时取样,最后利用薄层色谱(Thin layer chromatography,TLC)分析不同降解时间下褐藻胶降解的产物分布。
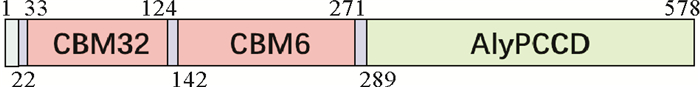
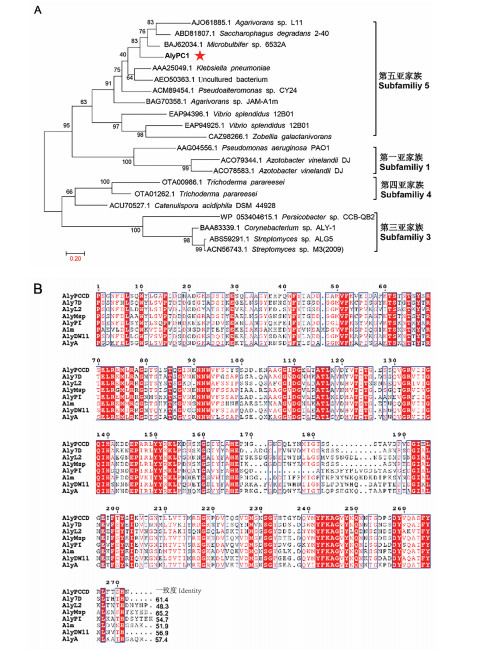
2 实验结果 2.1 AlyPC1序列分析从Pseudoalteromonas sp. 01中克隆出一种褐藻胶裂解酶基因alypc1,GeneBank收录号为ON112080。该酶的cDNA共计1 737 bp, 编码578个氨基酸残基,去掉信号肽后,AlyPC1的理论分子量为61 kDa。经在线软件SignalP 5.0预测出AlyPC1的前22个氨基酸残基(Met1-Gly22)为信号肽。如图 1所示,AlyPC1是一个多结构域褐藻胶裂解酶,有2个非催化结构域以及一个催化结构域构成,其中2个非催化结构域分别为CBM32和CBM6。系统发育树(见图 2A)表明,AlyPC1属于PL7家族第5亚家族。同时,多序列比对(见图 2B)表明,AlyPC1的催化结构域AlyPCCD的氨基酸序列同来源于Microbulbifer sp. 6532A的AlyMsp[18]的氨基酸序列相似性最高,约为65.2%。
|
图 1 AlyPC1结构域示意图 Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of modular organization |
|
( A:AlyPC1系统进化树;B:AlyPC1的催化结构域AlyPCCD与PL7褐藻胶裂解酶一级序列比对。图B中所有序列的来源信息同图A中的一致。A: The phylogenetic tree of AlyPC1; B: Multiple amino acid sequence alignment of AlyPC1 and other alginate lyases of PL7 sub.5. The source information for all sequences in Figure B is consistent with that in Figure A. ) 图 2 AlyPC1序列分析 Fig. 2 The sequence analysis of AlyPC1 |
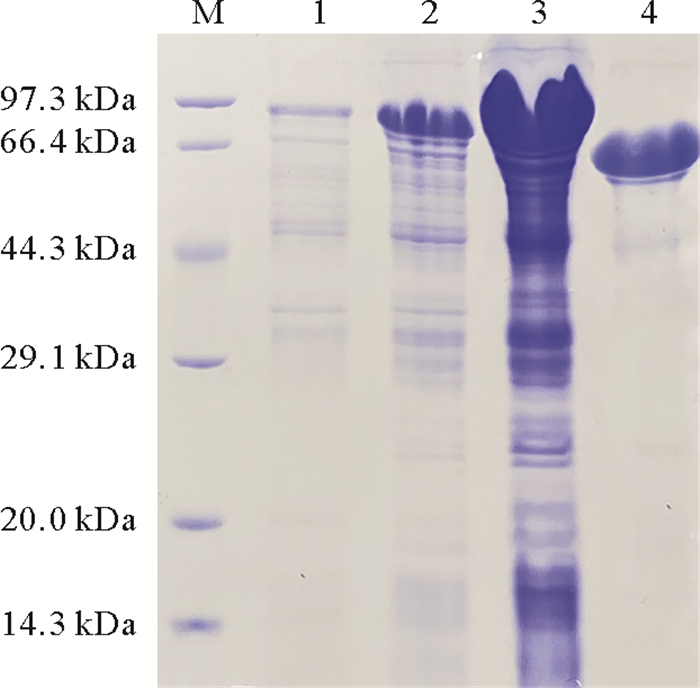
将克隆的alypc1片段与pET32a-p载体质粒连接后转化至E. coli BL21(DE3)中,融合蛋白在16 ℃诱导表达20 h。如图 3第2、3泳道所示,融合蛋白AlyPC1能够正确表达,且为可溶性蛋白。SDS-PAGE电泳结果如图 3第4泳道所示,可通过Ni-NTA琼脂糖凝胶纯化并用Prescission蛋白酶酶切后可以获得纯度较高的AlyPC1,分子量为61 kDa,同预测分子量相近。经计算,1 L菌体培养液可获得20 mg纯化蛋白。
|
( M:蛋白标准品;1:未诱导菌体;2:IPTG诱导后菌体;3:菌体超声破碎后上清液;4:经纯化-蛋白酶酶切后的目的蛋白AlyPC1。M: Protein marker; 1: The bacterium before induction; 2: The bacterium after induction by IPTG; 3. The supernatant after sonication; 4. The protein AlyPC1 after purification and Prescission digestion. ) 图 3 AlyPC1的SDS-PAGE电泳检测结果 Fig. 3 SDS-PAGE analysis of AlyPC1 |
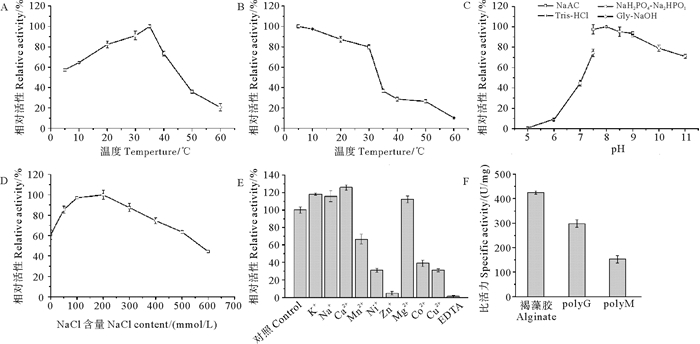
如图 4A所示: AlyPC1最适反应温度为35 ℃,在5 ℃时其酶活性仅为其最高酶活性的60%;高于40 ℃时其酶活性迅速下降;在60 ℃时其酶活性仅为其最高活性的20%。将AlyPC1置于5~60 ℃孵育1 h,通过测定剩余活性验证AlyPC1的稳定性(见图 4B),AlyPC1在低于30 ℃条件下孵育后,酶活性保留了约80%,但是随温度升高,孵育后剩余活性降低,在40 ℃孵育后活性仅剩30%左右。如图 4C所示,AlyPC1最适反应pH为8.0,且pH在7.5~9.0之间时其酶活性保留90%以上。综上所述,AlyPC1在适中温度以及较为宽泛的pH范围内发挥作用,具有开发成为工具酶的潜能。
|
( A:温度对AlyPC1活性的影响;B:AlyPC1温度稳定性;C:pH对AlyPC1活性的影响;D:NaCl浓度对AlyPC1活性的影响;E:金属离子对AlyPC1活性的影响;F:AlyPC1底物特异性。A: The effect of temperature on the enzymatic activity of AlyPC1; B: The thermal stability of AlyPC1; C: The effect of pH on the enzymatic activity AlyPC1; D: The effect of NaCl concentration on the activity of AlyPC1; E: Effects of metal ions on the activity of AlyPC1; F: Substrate specificity of AlyPC1. ) 图 4 AlyPC1的酶学性质 Fig. 4 Characterization of AlyPC1 |
NaCl含量对AlyPC1活性的影响如图 4D所示,反应体系含有NaCl 200 mmol/L时的酶活最高;反应体系中不添加NaCl时的酶活性仅为反应体系中含有NaCl 200 mmol/L时的酶活性的60%。同时,本研究中测定了不同金属离子对于AlyPCL酶活性的影响(见图 4E),K+、Na+、Ca2+和Mg2+对于AlyPC1的酶活性有轻微的促进作用。相反,Mn2+、Ni2+、Zn2+、Co2+、Cu2+以及EDTA能够明显抑制AlyPC1的酶活性。
此外,如图 4F所示,AlyPC1能够有效地降解褐藻胶、polyG以及polyM三种底物,比活力分别为425.4、298.6和152.5 U/mg,表明AlyPC1为双功能褐藻胶裂解酶[8]。
2.4 AlyPC1对褐藻胶的降解过程AlyPCl降解褐藻胶如图 5所示:前30 min内,AlyPCl随机切断褐藻胶,从而产生聚合度较高的褐藻寡糖,此时产生的寡糖以四糖为主,表明AlyPC1是一个内切型褐藻胶裂解酶;30 min后,小分子量的褐藻寡糖降解后的主要产物为三糖,最终的反应产物中含有二糖、三糖以及四糖。
|
图 5 TLC检测AlyPC1降解褐藻胶随时间变化的产物 Fig. 5 Time-course of alginate degradation by AlyPC1 was analyzed by TLC |
AlyPC1最适反应温度为35 ℃,在低于30 ℃条件下可以稳定存在1 h,说明AlyPC1在较为适中的温度下发挥作用。PL6家族的TsAly6A最适反应温度为35 ℃,但是在10和20 ℃下的酶活性分别是最大活性的21.1%和73.1%[19];而相同条件下,AlyPC1的酶活性分别是最高活性的64.4%和82.2%,这说明AlyPC1在室温下更具有优势,有利于降低制备寡糖的成本。另外,来自于同家族的rPyAly[20]和AlyD[21]最适反应pH均为8.0,但是在pH=7.5以及pH=9.0时,rPyAly[20]和AlyD[21]的酶活性分别是其最大活性的80%和60%[21];而相同反应条件下,AlyPC1能够保留其最高活性的90%以上,表明AlyPC1能够在较为宽泛的pH范围内发挥作用,降低了反应过程对缓冲液pH的需求。
AlyPC1可以降解褐藻胶、polyG以及polyM,但降解效率不同,证明AlyPC1是一个有偏好性的双功能的褐藻胶裂解酶。各种形式的褐藻胶均可作为AlyPC1的底物,说明AlyPC1可以充分利用资源。
| [1] |
Inoue A, Ojima T. Functional identification of alginate lyase from the brown alga Saccharina japonica[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 4937. DOI:10.1038/s41598-019-41351-6 (  0) 0) |
| [2] |
Bixler H J, Porse H. A decade of change in the seaweed hydrocolloids industry[J]. Journal of Applied Phycology, 2010, 23(3): 321-335. (  0) 0) |
| [3] |
George M, Abraham T E. Polyionic hydrocolloids for the intestinal delivery of protein drugs: Alginate and chitosan—a review[J]. Journal of Controlled Release, 2006, 114(1): 1-14. DOI:10.1016/j.jconrel.2006.04.017 (  0) 0) |
| [4] |
Lee K Y, Mooney D J. Alginate: Properties and biomedical applications[J]. Progress in Polymer Science, 2012, 37(1): 106-126. DOI:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2011.06.003 (  0) 0) |
| [5] |
Wang M, Chen L, Zhang Z. Potential applications of alginate oligosaccharides for biomedicine—A mini review[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2021, 271: 118408. DOI:10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118408 (  0) 0) |
| [6] |
Zhang C, Li M, Rauf A, et al. Process and applications of alginate oligosaccharides with emphasis on health beneficial perspectives[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 2023, 63: 1-27. DOI:10.1080/10408398.2021.1939649 (  0) 0) |
| [7] |
Zhang C, Wang W, Zhao X, et al. Preparation of alginate oligosaccharides and their biological activities in plants: A review[J]. Carbohydrate Research, 2020, 494: 108056. DOI:10.1016/j.carres.2020.108056 (  0) 0) |
| [8] |
Xing M, Cao Q, Wang Y, et al. Advances in research on the bioactivity of alginate oligosaccharides[J]. Marine Drugs, 2020, 18(3): 144. DOI:10.3390/md18030144 (  0) 0) |
| [9] |
Zhang Y H, Shao Y, Jiao L, et al. Characterization and application of an alginate lyase, Aly1281 from marine bacterium Pseudoalteromonas carrageenovora ASY5[J]. Marine Drugs, 2020, 18(2): 95. DOI:10.3390/md18020095 (  0) 0) |
| [10] |
Wong T Y, Preston L A, Schiller N L. Alginate lyase: Review of major sources and enzyme characteristics, structure-function analysis, biological roles, and applications[J]. Annual Review of Microbiology, 2000, 54: 289-340. DOI:10.1146/annurev.micro.54.1.289 (  0) 0) |
| [11] |
Xu F, Chen X L, Sun X H, et al. Structural and molecular basis for the substrate positioning mechanism of a new PL7 subfamily alginate lyase from the arctic[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2020, 295(48): 16380-16392. DOI:10.1074/jbc.RA120.015106 (  0) 0) |
| [12] |
Ushasree M V, Lee O K, Lee E Y. Alginate derived functional oligosaccharides: Recent developments, barriers, and future outlooks[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2021, 267: 118158. DOI:10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118158 (  0) 0) |
| [13] |
Zhang K, Liu T, Liu W, et al. Structural insights into the substrate-binding cleft of AlyF reveal the first long-chain alginate-binding mode[J]. Acta Crystallographica Section D, 2021, 77(3): 336-346. DOI:10.1107/S205979832100005X (  0) 0) |
| [14] |
Zhang K, Yang Y, Wang W, et al. Substrate-binding mode and intermediate-product distribution coguided protein design of alginate lyase AlyF for altered end-product distribution[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2021, 69(25): 7190-7198. DOI:10.1021/acs.jafc.1c02473 (  0) 0) |
| [15] |
Haug A, Larsen B, Smidsrod O. Studies on the sequence of uronic acid residues in alginic acid[J]. Acta Chemica Scandinavica, 1967, 21(3): 691-704. (  0) 0) |
| [16] |
Letunic I, Khedkar S, Bork P. SMART: Recent updates, new developments and status in 2020[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2021, 49(D1): 458-460. DOI:10.1093/nar/gkaa937 (  0) 0) |
| [17] |
Lyu Q, Zhang K, Zhu Q, et al. Structural and biochemical characterization of a multidomain alginate lyase reveals a novel role of CBM32 in CAZymes[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA), 2018, 1862(9): 1862-1869. DOI:10.1016/j.bbagen.2018.05.024 (  0) 0) |
| [18] |
Swift S M, Hudgens J W, Heselpoth R D, et al. Characterization of AlgMsp, an alginate lyase from Microbulbifer sp. 6532A[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(11): e112939. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0112939 (  0) 0) |
| [19] |
Gao S, Zhang Z, Li S, et al. Characterization of a new endo-type polysaccharide lyase (PL) family 6 alginate lyase with cold-adapted and metal ions-resisted property[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2018, 120(Pt A): 729-735. (  0) 0) |
| [20] |
Akira I, Chieco M, Toshiki U, et al. Characterization of an eukaryotic PL-7 alginate lyase in the marine red[J]. Current Biotechnology, 2015, 4(3): 240-248. DOI:10.2174/2211550104666150915210434 (  0) 0) |
| [21] |
Badur A H, Jagtap S S, Yalamanchili G, et al. Alginate lyases from alginate-degrading Vibrio splendidus 12B01 are endolytic[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2015, 81(5): 1865-1873. DOI:10.1128/AEM.03460-14 (  0) 0) |
 2024, Vol. 54
2024, Vol. 54


