| 磁性分子印迹聚合物在食品安全检测中的应用 |
食品在生产、加工和储存过程中,有时会被药物等污染,这些问题食品对人体产生危害的过程是缓慢的、累积性的,人们往往意识不到这些危害。除此之外,不法商贩在食品生产加工过程中滥用药物、添加剂等行为也屡禁不止。尽管我国已制定了相关法规和食品安全监管措施,但食品安全现状仍令人担忧,主要表现为:农业中农药残留量超标,畜牧业中抗生素、激素超标,食品加工业中滥用食品添加剂甚至有毒化工产品等。因此,人们逐渐认识到食品安全检测的重要性。目前,常用的食品安全检测技术主要有高效液相色谱技术[1]、电化学检测技术[2]、光谱分析法[3]等。其中,高效液相色谱法是目前最常见的方法。由于食品基质复杂,有害物含量低,分析前需要进行有效的净化和浓缩,以消除干扰,提高分析结果的准确性和灵敏度。
传统的样品前处理方法有液液萃取[4-5]、固相萃取[6-7]等,其中固相萃取法是最常用的方法。但这些方法对目标物缺乏选择性,为了提高目标物的纯度,需要增加样品的净化步骤,因此存在溶剂使用量大、处理时间长、操作繁琐等缺点。因此,开发一种高效的样品前处理方法以及制备一种高选择性的材料具有重要意义。
1 磁性分子印迹聚合物概念分子印迹技术(Molecular Imprinting Technique,MIT)来源于免疫学中抗原与抗体的概念。分子印迹聚合物(Molecularly Imprinted Polymers,MIPs)是在模板分子存在的情况下,加入功能单体交联聚合后,采用物理方法或化学方法从聚合物中除去模板分子而获得与模板分子在形状、大小、作用位点互补的孔穴[8-10]。MIPs具有物理和化学稳定性高、易于制备、成本低和可重复利用等显著优点,在低浓度或复杂基质中也能高选择性地富集目标物,已被广泛应用于色谱分离[11]、固相萃取[12-13]、化学传感器[14]和催化[15]等领域。然而,MIPs在应用时要经过破碎、筛分以及高速离心等处理程序,从而使目标分子的传质受到阻碍,导致亲和结合力低,耗时、耗力[16-17]。近年来,磁性分子印迹聚合物(Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymers,MMIPs)用于样品前处理过程得到越来越多的关注。MMIPs的制备过程主要包括磁性纳米粒子的制备和表面改性,以及涂覆分子印迹聚合物。由于加入了磁性介质,MMIPs可以在外加磁场的作用下,不经过离心或过滤就能实现与基质的快速分离,因此在食品安全样品前处理领域得到广泛应用[18]。
2 磁性分子印迹聚合物的制备方法磁性分子印迹聚合物制备方法主要有:本体聚合法、悬浮聚合法、乳液聚合法、沉淀聚合法和表面印迹聚合法。表 1为常见的磁性分子印迹聚合物的制备方法及其优缺点。
| 表 1 常见的磁性分子印迹聚合物的制备方法及其优缺点 |
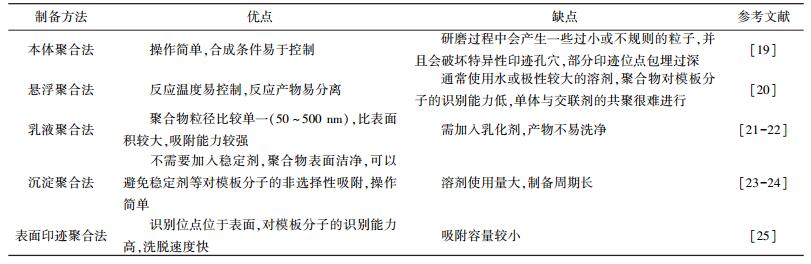 |
3 磁性分子印迹聚合物在食品安全检测中的应用
MMIPs作为固相萃取材料用于样品前处理过程,克服了传统液-液萃取法溶剂用量多的缺点;且对被测目标物具有特异性,可以有效消除其他杂质的干扰,检测限较低。同时,由于加入磁性介质可以快速实现检测试剂与样品基质的分离,明显缩短了操作时间、提高了效率,因此MMIPs已被广泛用于食品安全检测。表 2总结归纳了磁性分子印迹聚合物在食品安全检测中的应用。
| 表 2 磁性分子印迹聚合物在食品安全检测中的应用 |
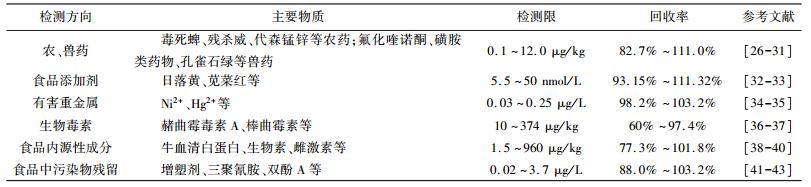 |
4 总结与展望
因具有在低浓度或复杂基质中快速分离目标物以及特异性识别等特点,磁性分子印迹聚合物已被广泛应用于食品安全检测领域,但仍存在一些需要改进的问题,例如:1)需要开发更多种类的功能单体和交联剂;2)目前一般用于检测小分子,而很少用于检测蛋白质和部分微生物;3)分子印迹聚合物对磁载体的包裹不完全,存在磁泄露问题。随着化学合成技术的不断发展,上述问题终将得到解决,磁性分子印迹聚合物将在食品安全检测领域发挥更加重要的作用。
| [1] |
MICHAELA P, PETERŠ. Determination and occurrence of 5-hydroxymethyl-2-furaldehyde in white and brown sugar by high performance liquid chromatography[J]. Food Control, 2017, 78: 183-186. DOI:10.1016/j.foodcont.2017.02.059 |
| [2] |
ABDALHAI M H, FERNANDES A M, XIA X, et al. Electrochemical genosensor to detect pathogenic bacteria (escherichia coli O157:H7) as applied in real food samples (fresh beef) to improve food safety and quality control[J]. Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry, 2015, 63(20): 5017-5025. |
| [3] |
OßMANN B E, SARAU G, SCHMITT S W, et al. Development of an optimal filter substrate for the identification of small microplastic particles in food by micro-Raman spectroscopy[J]. Analytical & Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2017(6): 1-11. |
| [4] |
GIL'DEEVA G N, BELOSTOTSKⅡ A V, SAPOZHNIKOVA D S. Development and validation of an HPLC method with mass spectrometric detection for quantitative determination of chlormadinone acetate and ethinyl Estradiol in human blood plasma[J]. Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal, 2017, 51(2): 1-11. |
| [5] |
HAMED A M, MORENO-GONZÁLEZ D, GARCÍA-CAMPA-A A M, et al. Determination of aflatoxins in yogurt by dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction and HPLC with photo-induced fluorescence detection[J]. Food Analytical Methods, 2017, 10(2): 516-521. DOI:10.1007/s12161-016-0611-6 |
| [6] |
ANSARI S A, MOHAPATRA P K. A review on solid phase extraction of actinides and lanthanides with amide based extractants[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2017, 1499: 1-20. DOI:10.1016/j.chroma.2017.03.035 |
| [7] |
HOU X, WANG X, SUN Y, et al. Graphene oxide for solid-phase extraction of bioactive phenolic acids[J]. Analytical & Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2017, 409(14): 3541-3549. |
| [8] |
INANAN T, TVZMEN N, AKGÖL S, et al. Selective cholesterol adsorption by molecular imprinted polymeric nanospheres and application to GIMS[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2016, 92: 451-460. DOI:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.07.007 |
| [9] |
CULVER H R, STEICHEN S D, PEPPAS N A. A closer look at the impact of molecular imprinting on adsorption capacity and selectivity for protein templates[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2016, 17(12): 4045-4053. DOI:10.1021/acs.biomac.6b01482 |
| [10] |
MARTINEZSENA T, ARMENTA S, GUARDIA M, et al. Determination of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in water and urine using selective molecular imprinted polymer extraction and liquid chromatography[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biomedical Analysis, 2016, 131: 48-53. |
| [11] |
WANG Z, CAO X. Preparation of core-shell molecular imprinting polymer for lincomycin A and its application in chromatographic column[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2015, 50(7): 1136-1145. DOI:10.1016/j.procbio.2015.04.013 |
| [12] |
MARÍA C B A, NEREA O L, PILAR B B. Solid phase extraction using molecular imprinted polymers for phthalate determination in water and wine samples by HPLC-ESI-MS[J]. Microchemical Journal, 2017, 132: 233-237. DOI:10.1016/j.microc.2017.02.007 |
| [13] |
WANG H, WANG R, HAN Y. Preparation of molecular imprinted microspheres based on inorganic-organic co-functional monomer for miniaturized solid-phase extraction of fluoroquinolones in milk[J]. Journal of Chromatography B, 2014, 949-950(4): 24-29. |
| [14] |
ZHOU Z, YING H, LIU Y, et al. Synthesis of surface molecular imprinting polymer on SiO2-coated CdTe quantum dots as sensor for selective detection of sulfadimidine[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2017, 404: 188-196. DOI:10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.01.249 |
| [15] |
KARAKHANOV E A, MAXIMOV A L. Molecular imprinting technique for the design of cyclodextrin based materials and their application in catalysis[J]. Current Organic Chemistry, 2017, 14(13): 1284-1295. |
| [16] |
LIN Z Z, ZHANG H Y, PENG A H, et al. Determination of malachite green in aquatic products based on magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers[J]. Food Chemistry, 2016, 200: 32-37. DOI:10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.01.001 |
| [17] |
NING F, PENG H, DONG L, et al. Preparation and characterization of superparamagnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for selective adsorption and separation of vanillin in food samples[J]. Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry, 2014, 62(46): 11138-11145. |
| [18] |
XIE L, GUO J, ZHANG Y, et al. Novel molecular imprinted polymers over magnetic mesoporous silica microspheres for selective and efficient determination of protocatechuic acid in Syzygium aromaticum[J]. Food Chemistry, 2015, 178: 18-25. DOI:10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.01.069 |
| [19] |
DÍAZ-BAO M, REGAL P, BARREIO R, et al. A facile method for the fabrication of magnetic molecularly imprinted stir-bars:A practical example with aflatoxins in baby foods[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2016, 1471: 51-59. DOI:10.1016/j.chroma.2016.10.022 |
| [20] |
LIU M, LI X Y, LI J J, et al. Synthesis of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for the selective separation and determination of metronidazole in cosmetic samples[J]. Analytical & Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2015, 407(13): 3875-3880. |
| [21] |
MAO Y, CUI J, ZHAO J, et al. Selective separation of bifenthrin by pH-sensitive/magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers prepared by Pickering emulsion polymerization[J]. Fibers & Polymers, 2016, 17(10): 1531-1539. |
| [22] |
ZHU Y, JIANG D, SUN D, et al. Fabrication ofmagnetic imprinted sorbents prepared by Pickering emulsion polymerization for adsorption of erythromycin from aqueous solution[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2016, 4(3): 3570-3579. DOI:10.1016/j.jece.2016.07.036 |
| [23] |
MA W, LI S, CHEN L, et al. Core-shell thermal-responsive and magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers based on mag-yeast for selective adsorption and controlled release of tetracycline[J]. Journal of the Iranian Chemical Society, 2017, 14(1): 209-219. DOI:10.1007/s13738-016-0971-2 |
| [24] |
PEBDANI A A, SHABANI A M H, DADFARNIA S. Selective separation anddetermination of diclofenac via magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer and spectrophotometry[J]. Journal of the Iranian Chemical Society, 2016, 13(1): 155-164. DOI:10.1007/s13738-015-0723-8 |
| [25] |
NING F, QIU T, WANG Q, et al. Dummy-surface molecularly imprinted polymers on magnetic graphene oxide for rapid and selective quantification of acrylamide in heat-processed (including fried) foods[J]. Food Chemistry, 2016, 221: 1797. |
| [26] |
YAO G H, LIANG R P, HUANG C F, et al. Surface plasmon resonance sensor based on magnetic molecularly imprinted polymersamplification for pesticide recognition[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2013, 85(24): 11944-11951. DOI:10.1021/ac402848x |
| [27] |
GAO L, CHEN L, LI X. Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers based on carbon nanotubes for extraction of carbamates[J]. Microchimica Acta, 2015, 182(3-4): 1-7. |
| [28] |
KUMAR S, KARFA P, PATRA S, et al. Molecularly imprinted star polymer-modified superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle for trace level sensing and separation of mancozeb[J]. Rsc Advances, 2016, 6(43): 36751-36760. DOI:10.1039/C6RA03204D |
| [29] |
LIN Z Z, ZHANG H Y, LI L, et al. Application of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers in the detection of malachite green in fish samples[J]. Reactive & Functional Polymers, 2016, 98: 24-30. |
| [30] |
MOHAMMAD K, FOROUZAN A, HAMID R L Z, et al. Determination of sulfonamides in chicken meat by magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer coupled to HPLC-UV[J]. Food Analytical Methods, 2014, 7(1): 73-80. DOI:10.1007/s12161-013-9600-1 |
| [31] |
XIAO D, DRAMOU P, XIONG N, et al. Preparation of molecularly imprinted polymers on the surface of magnetic carbon nanotubes with a pseudo template for rapid simultaneous extraction of four fluoroquinolones in egg samples[J]. Analyst, 2013, 138(11): 3287-3296. DOI:10.1039/c3an36755j |
| [32] |
ARVAND M, ERFANIFAR Z, ARDAKI M S. A new vore@shell silica-coated magnetic molecular imprinted nanoparticles for selective detection of sunset yellow in food samples[J]. Food Analytical Methods, 2017, 10(7): 2593-2606. DOI:10.1007/s12161-017-0803-8 |
| [33] |
HAN Q, WANG X, YANG Z, et al. Fe3O4@rGO doped molecularly imprinted polymer membrane based on magnetic field directed self-assembly for the determination of amaranth[J]. Talanta, 2014, 123(9): 101-108. |
| [34] |
ASGHARINEZHAD A A, JALILIAN N, EBRAHIMZADEH H, et al. A simple and fast method based on new magnetic ion imprinted polymer nanoparticles for the selective extraction of Ni ions in different food samples[J]. Rsc Advances, 2015, 5(56): 45510-45519. DOI:10.1039/C5RA05639J |
| [35] |
NAJAFI E, ABOUFAZELI F, ZHAD H R, et al. A novel magnetic ion imprinted nano-polymer for selective separation and determination of low levels of mercury(Ⅱ) ions in fish samples[J]. Food Chemistry, 2013, 141(4): 4040-4045. DOI:10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.06.118 |
| [36] |
TURAN E, şAHIN F. Molecularly imprinted biocompatible magnetic nanoparticles for specific recognition of Ochratoxin A[J]. Sensors & Actuators B Chemical, 2016, 227: 668-676. |
| [37] |
PATRICIA R, MÓNICA D B, ROCÍO B, et al. Design of a molecularly imprinted stir-bar for isolation of patulin in apple and LC-MS/MS detection[J]. Separations, 2017, 4(2): 11-16. DOI:10.3390/separations4020011 |
| [38] |
LI X, ZHANG B, TIAN L, et al. Improvement of recognition specificity of surface protein-imprinted magnetic microspheres by reducing nonspecific adsorption of competitors using 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine[J]. Sensors & Actuators B Chemical, 2015, 208: 559-568. |
| [39] |
UZURIAGA-SÁNCHEZ R J, KHAN S, WONG A, et al. Magnetically separable polymer (Mag-MIP) for selective analysis of biotin in food samples[J]. Food Chemistry, 2016, 190(5): 460-467. |
| [40] |
LAN H, GAN N, PAN D, et al. An automated solid-phase microextraction method based on magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer as fiber coating for detection of trace estrogens in milk powder[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2014, 1331(3): 10-18. |
| [41] |
LI C, MA X, ZHANG X, et al. Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles-based solid-phase extraction coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for selective determination of trace di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate in water samples[J]. Analytical & Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2016, 408(27): 1-8. |
| [42] |
HE D, ZHANG X, GAO B, et al. Preparation of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer for the extraction of melamine from milk followed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Food Control, 2014, 36(1): 36-41. DOI:10.1016/j.foodcont.2013.07.044 |
| [43] |
YUAN Y, YAN L, TENG W, et al. Preparation of core-shell magnetic molecular imprinted polymer with binary monomer for the fast and selective extraction of bisphenol A from milk[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2016, 1462: 2-7. DOI:10.1016/j.chroma.2016.06.045 |
 2018, Vol. 32
2018, Vol. 32


