我国催化重整装置每年副产大量的C10芳烃,其中含有丰富的均四甲苯(durene,1, 2, 4, 5-四甲基苯)。均四甲苯分子式为C10H12,是一种重要的化工原料,为具有樟脑味的白色晶体,不溶于水。均四甲苯主要用途是合成均酐(pyromellitic dianhydride,均苯四甲酸二酐)[1],均酐是合成聚酰亚胺的原料,聚酰亚胺是一种性能优越的新型合成材料,广泛应用于航空航天及国防等领域[2]。近年,随着聚酰亚胺需求量的增大,对均四甲苯的开发研究成为热点。均四甲苯的生产方法主要是合成法及分离法,合成法复杂、成本高;分离法以C10芳烃为原料,从中分离得到符合市场需求的均四甲苯单品。本课题组以C10芳烃为原料,已初步得到均四甲苯粗产品,粗产品中主要杂质为均四甲苯的2种同分异构体(1, 2, 3, 4-四甲基苯及1, 2, 3, 5-四甲基苯),由于三者沸点极其接近,精馏法不能经济有效地分离,因此为提高均四甲苯的纯度,拟采用重结晶对均四甲苯粗产品进行精制。目前关于均四甲苯的溶解度数据未见报道。本文重点研究了均四甲苯在9种溶剂中的溶解度,从而为结晶过程的开发设计提供指导。
溶解度的测定包括静态平衡法[3-5]及动态法[6-8]。基于动态法高效易操作且均四甲苯具有升华性的特点,本文采用动态法测定温度在283.15~308.15 K时均四甲苯在甲醇、乙醇、异丙醇、正丁醇、乙腈、丙酮、乙酸乙酯、乙酸正丁酯及乙酸异戊酯9种纯溶剂中的溶解度,并用改进的Apelblat方程[9]、λh方程[10]及活度系数模型(NRTL方程[11]及Wilson方程[12])对实验数据进行关联。此外,基于Wilson模型的参数拟合值及实验数据,确定混合过程的溶解吉布斯自由能ΔmixG,溶解焓ΔmixH和溶解熵ΔmixS。本文工作可为均四甲苯的结晶过程提供理论指导。
2 实验材料和方法 2.1 实验仪器电子分析天平(精度0.1 mg),FB224型,上海舜宇恒平科学仪器有限公司;差示扫描量热分析仪(DSC),1090B型,美国TA仪器公司;热重分析仪(TGA),TA Q500 TGA型,美国TA仪器公司;恒温磁力搅拌器,85-2型,上海司乐仪器有限公司;低温恒温槽,DC-0520型,上海舜宇恒平科学仪器有限公司。
2.2 实验试剂均四甲苯(纯度≥98%,上海麦克林生物科技有限公司);甲醇、异丙醇、正丁醇、丙酮、乙酸乙酯及乙酸异戊酯(均为分析纯,上海泰坦通用试剂);乙醇(分析纯,阿拉丁试剂有限公司);乙腈(色谱纯,上海天莲化工科技有限公司);乙酸正丁酯(分析纯,上海凌峰化学试剂有限公司)。
2.3 实验装置和方法1) TGA曲线测定
采用热重分析仪在氮气气氛中分析均四甲苯的热稳定性,从室温开始,以5 K·min-1的升温速率升温至373.15 K,得到TGA曲线。
2) DSC曲线测定
称取一定量的均四甲苯样品置于铝制密封坩埚中,氮气作为保护气,以5 K·min-1的升温速率从室温升至373.15 K,得到均四甲苯DSC曲线。
3) 溶解度的测定
采用动态法测得均四甲苯的溶解度数据,以最后一片晶体的溶解作为判断溶液是否达到饱和的依据[13],实验装置如图 1所示。
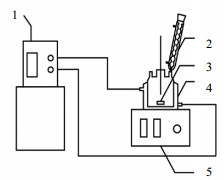
|
图 1 溶解度测定装置 Fig.1 Schematic diagram of the experimental setup for solubility measurements 1. cryogenic bath 2. condenser 3. stir bar 4. jacketed flask 5. magnetic stirrers |
开启冷凝水装置,称取一定量的均四甲苯于夹套瓶中,并加入30 g溶剂,放入磁子,开启磁力搅拌,在设置的温度下搅拌至固体完全溶解,继续分批加入少量(≤0.02 g,约1.5×10-4 mol)的固体,直至某批次加入的固体搅拌2 h后仍未完全溶解,则认为溶液达到饱和。计算所加入固体的总质量,依据式(1)计算均四甲苯溶解度,每组至少测定3次,取平均值作为溶解度数据。根据同样的方法测定均四甲苯在不同溶剂及不同温度下的溶解度数据。
| ${x_{\rm{1}}} = \frac{{{m_{\rm{1}}}/{M_{\rm{1}}}}}{{{m_{\rm{1}}}/{M_{\rm{1}}} + {m_{\rm{2}}}/{M_{\rm{2}}}}}$ | (1) |
式中:x1为溶质的摩尔溶解度,m1、m2分别为饱和溶液中溶质和溶剂的质量,M1、M2分别为溶质及溶剂的相对分子质量。
2.4 热力学模型以活度系数定量表示液固平衡,将液相活度系数应用于达到液固相平衡体系中的液相,可精确地描述溶解度[14]。普遍化的溶解度方程可表示为
| $ \ln \left(x_{i} \gamma_{i}\right)=\frac{\Delta H_{\mathrm{tp}}}{R}\left(\frac{1}{T_{\mathrm{tp}}}-\frac{1}{T}\right)-\frac{\Delta c_{p}}{R}\left(1-\frac{T_{t \mathrm{p}}}{T}+\ln \frac{T_{\mathrm{tp}}}{T}\right)-\frac{\Delta V}{R T}\left(p-p_{\mathrm{tp}}\right) $ | (2) |
式中:下标tp表示三相点,xi为溶质i的摩尔溶解度,γi为溶质i在液相中的活度系数,T为绝对温度,p为绝对压力,ΔHtp为三相点时的熔化焓,Δcp为比定压热容差,ΔV为摩尔体积变化,R为理想气体常数。
通常压力的修正可忽略,且热容差的影响很小[15],三相点的温度Ttp可用大气压下溶质的熔点代替,因此溶解度方程可简化为
| $ \ln \left(x_{i} \gamma_{i}\right)=\frac{\Delta H_{\mathrm{m}, i}}{R}\left(\frac{1}{T_{\mathrm{m}, i}}-\frac{1}{T}\right) $ | (3) |
式中:ΔHm, i为溶质的熔化焓,Tm, i为溶质i的熔点。
2.4.1 改进的Apelblat方程改进的Apelblat方程[16]广泛应用于溶解度的数据关联,该方程由Clausius-Clapeyron方程得到[17],方程形式为
| $\ln {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {x_1} = A + \frac{B}{T} + C\ln {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} T$ | (4) |
式中:A、B、C为3个模型参数,参数A和B反映了溶液的非理想性对溶解度的影响,C体现了温度与熔化焓的关系[18]。
2.4.2 λh方程λh方程为半经验模型[19],由Buchowski首次提出,方程形式为
| $ \ln \left[1+\frac{\lambda\left(1-x_{1}\right)}{x_{1}}\right]=\lambda h\left(\frac{1}{T}-\frac{1}{T_{\mathrm{m}}}\right) $ | (5) |
式中:λ和h为模型回归参数,Tm为溶质熔点。
2.4.3 Wilson方程Grant M. Wilson于1964年提出Wilson方程。对于二元混合溶液,Wilson模型的形式为[20]
| $ \ln {\gamma _1} = - \ln \left( {{x_1} + {\mathit{\Lambda } _{12}}{x_2}} \right) + {x_2}\left( {\frac{{{\mathit{\Lambda }_{12}}}}{{{x_1} + {\mathit{\Lambda }_{12}}{x_2}}} - \frac{{{\mathit{\Lambda }_{21}}}}{{{x_2} + {\mathit{\Lambda }_{21}}{x_1}}}} \right) $ | (6) |
其中
| ${\mathit{\Lambda } _{12}} = \frac{{{V_2}}}{{{V_1}}}\exp {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} \frac{{ - {\lambda _{12}}}}{{RT}}$ | (7) |
| ${\mathit{\Lambda } _{21}} = \frac{{{V_1}}}{{{V_2}}}\exp {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} \frac{{ - {\lambda _{21}}}}{{RT}}$ | (8) |
| ${\lambda _{12}} = {g_{12}} - {g_{11}}$ | (9) |
| ${\lambda _{21}} = {g_{21}} - {g_{22}}$ | (10) |
式中:γ1为溶质的活度系数,x2为液体中溶剂的摩尔浓度,V1和V2分别为液体中组分1和组分2的摩尔体积,Λ12和Λ21为Wilson参数,g12- g11及g21- g22为Wilson方程的二元交互参数。
2.4.4 NRTL方程以局部组成概念为基础,Renon和Prausnitz于1968年提出了NRTL模型[21]。NRTL方程广泛应用于溶解度的关联,对于二元体系,NRTL方程形式为
| $\ln {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\gamma _1} = {x_2}^2\left[ {\frac{{{\tau _{21}}{G_{21}}^2}}{{{{\left( {{x_1} + {x_2}{G_{21}}} \right)}^2}}} + \frac{{{\tau _{12}}{G_{12}}}}{{{{\left( {{x_2} + {x_1}{G_{12}}} \right)}^2}}}} \right]$ | (11) |
其中
| ${\tau _{12}} = \frac{{\left( {{g_{12}} - {g_{22}}} \right)}}{{RT}}$ | (12) |
| ${\tau _{21}} = \frac{{\left( {{g_{21}} - {g_{11}}} \right)}}{{RT}}$ | (13) |
| ${G_{12}} = \exp {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} \left( { - {a_{12}}{\tau _{12}}} \right)$ | (14) |
| ${G_{21}} = \exp {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} \left( { - {a_{21}}{\tau _{21}}} \right)$ | (15) |
式中:g12-g22及g21-g11为NRTL方程的交互参数,a12、a21为可调参数,该值表示溶液的非随机性,且a12=a21。
3 实验结果与讨论 3.1 TGA和DSC分析均四甲苯TGA曲线如图 2所示,均四甲苯起始失重温度为330 K,外延起始失重温度为369.9 K。因物质在熔点附近存在热失重现象,为降低热失重对DSC测试结果的影响,选用密闭坩埚对均四甲苯装样测试。
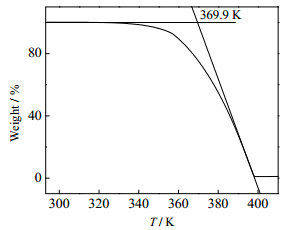
|
图 2 均四甲苯TGA曲线 Fig.2 TGA curve of durene |
DSC曲线如图 3所示,样品在温度为345 K时开始吸热,在330~345 K内样品在密闭坩埚中并未产生热效应,表明该温度范围内均四甲苯在环境中的热失重是物质挥发或升华引起的,且密闭坩埚的使用使样品的挥发或升华现象减弱,因而样品在330~345 K内未出现热效应。由DSC曲线可知,熔化终止温度约为360 K,该温度下均四甲苯在环境中的失重率很小,且密闭坩埚的使用可削弱热失重现象,进一步降低了热失重对DSC曲线准确度的影响,当温度达360 K之后曲线走平,表明在所测温度范围内样品热失重十分微弱,对DSC曲线的影响可忽略不计。若忽略测试温度范围内热失重对结果的影响,DSC曲线中的吸热峰由熔化过程产生,由图可得熔化温度Tm和熔化焓ΔfusHm。实验测得均四甲苯样品的熔点为354.05 K,熔化焓为19.24 kJ·mol-1,与文献报道[22]的熔点(352.35 K)及熔化焓值(20.97 kJ·mol-1)吻合良好。
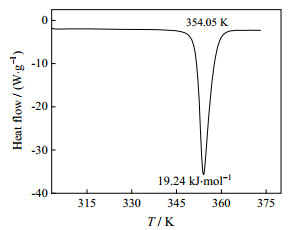
|
图 3 均四甲苯DSC曲线 Fig.3 DCS curve of durene |
在温度为283.15~308.15 K,均四甲苯在9种溶剂中的摩尔溶解度的实验测定值、4种模型计算值及实验值与计算值之间的偏差结果见表 1。结果表明,均四甲苯在9种纯溶剂中的溶解度随温度的升高而增大;在相同的温度下,均四甲苯在不同溶剂中溶解度的大小依次为:乙酸异戊酯 > 乙酸正丁酯 > 乙酸乙酯 > 丙酮 > 正丁醇 > 异丙醇 > 乙腈> 乙醇 > 甲醇。
|
|
表 1 均四甲苯在纯溶剂中的溶解度实验数据及拟合偏差 Table 1 Experimental data and fitting deviation of durene solubility in pure solvents |
利用相对偏差RD、平均相对偏差ARD及均方差RSMD来评估模型计算值与实验值之间的偏差,三者的方程形式如下
| ${\rm{RD}} = \frac{{\left| {{x_{i, {\rm{cal}}}} - {x_{i{\rm{, exp}}}}} \right|}}{{{x_{i{\rm{, exp}}}}}}$ | (16) |
| ${\rm{ARD}} = \frac{1}{n}\sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {\left| {\frac{{{x_{i, {\rm{cal}}}} - {x_{i{\rm{, exp}}}}}}{{{x_{i{\rm{, exp}}}}}}} \right|} $ | (17) |
| ${\rm{RMSD}} = \sqrt {\frac{{\sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {{{\left( {{x_{i, {\rm{cal}}}} - {x_{i{\rm{, exp}}}}} \right)}^2}} }}{n}} $ | (18) |
式中:xi, exp为摩尔溶解度的实验值,xi, cal为摩尔溶解度的模型关联计算值。
3.3 热力学模型4种方程的参数拟合值见表 2。采用相关系数R2描述4种模型的拟合度。
|
|
表 2 均四甲苯在不同纯溶剂中溶解度的模型参数回归值 Table 2 Fitting parameters of durene in different pure solvents |
结果表明:采用改进的Apelblat方程、λh方程、NRTL模型及Wilson模型关联所得相关系数R2分别不低于0.975、0.960、0.944及0.904,4种模型均能较好地关联均四甲苯在9种溶剂中的溶解度数据,所得模型方程可预测所测温度范围内均四甲苯在9种溶剂中的溶解度,并用于指导均四甲苯结晶过程;对比4种模型的关联结果,改进的Apelblat方程的关联效果最佳(ARD≤3.47%,RSMD≤0.22且R2≤0.975),改进的Apelblat方程关联曲线见图 4。
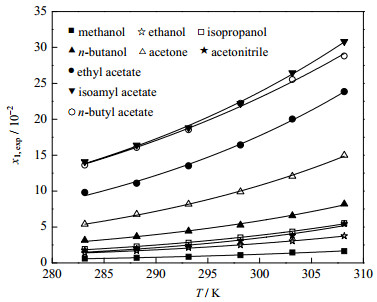
|
图 4 均四甲苯溶解度实验数据及改进的Apelblat模型关联 Fig.4 Experimental data of durene solubility and modified Apelblat model correlation |
根据实验数据及Wilson模型参数拟合值,可计算溶液的混合性质(ΔmixG,ΔmixH和ΔmixS),对于非理想溶液,混合性质为
| ${\Delta _{{\rm{mix}}}}M = {M^{\rm{E}}} + {\Delta _{{\rm{mix}}}}{M^{{\rm{id}}}}$ | (19) |
式中:M为G、H及S,ME为混合超额性质,ΔmixMid为理想溶液的混合性质。混合超额性质的计算式如下[23]:
| $ {G^{\rm{E}}} = - RT\left[ {{x_1}\ln \left( {{x_1} + {x_2}{\mathit{\Lambda }_{12}}} \right) + {x_2}\ln \left( {{x_2} + {x_1}{\mathit{\Lambda }_{21}}} \right)} \right] $ | (20) |
| $ H^{\mathrm{E}}=-T^{2}\left[\frac{\partial\left(G^{\mathrm{E}} / T\right)}{\partial T}\right] x_{1} x_{2}\left(\frac{\Delta \lambda_{12} \mathit{\Lambda }_{12}}{x_{1}+\mathit{\Lambda }_{12} x_{2}}+\frac{\Delta \lambda_{21} \mathit{\Lambda }_{21}}{x_{2}+\mathit{\Lambda }_{12} x_{1}}\right) $ | (21) |
| $ S^{\mathrm{E}}=\frac{H^{\mathrm{E}}-G^{\mathrm{E}}}{T} $ | (22) |
Mid根据Lewis-Randall规则计算。理想溶液的混合吉布斯自由能ΔmixG,混合熵ΔmixS及混合焓ΔmixH的计算式如下[24]:
| ${\Delta _{{\rm{mix}}}}{G^{{\rm{id}}}} = RT\left( {{x_1}\ln {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {x_1} + {x_2}\ln {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {x_2}} \right)$ | (23) |
| ${\Delta _{{\rm{mix}}}}{S^{{\rm{id}}}} = - R\left( {{x_1}\ln {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {x_1} + {x_2}\ln {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {x_2}} \right)$ | (24) |
| ${\Delta _{{\rm{mix}}}}{H^{{\rm{id}}}} = 0$ | (25) |
均四甲苯与有机溶剂(甲醇、乙醇、异丙醇、正丁醇、乙腈、丙酮、乙酸乙酯、乙酸丁酯及乙酸异戊酯)二元体系的混合性质(ΔmixG,ΔmixH和ΔmixS)的值见表 3。
|
|
表 3 均四甲苯在9种纯溶剂中的溶解热力学参数 Table 3 Thermodynamic parameters of durene dissolution in nine solvents |
由表 3可知,均四甲苯在9种纯溶剂的溶解过程中,ΔmixG值均小于0,溶解过程为自发过程,且该值的绝对值随温度的增加而增加,说明ΔmixG的大小体现了溶质溶解能力的大小;ΔmixH值均大于0,表明均四甲苯在9种纯溶剂中的溶解过程为吸热过程,因此解释了均四甲苯的溶解度随温度升高而增加的现象;ΔmixS值均大于0,表明均四甲苯的溶解过程为熵增过程,溶解过程中体系的混乱度增加。
4 结论(1) 在常压、温度为283.15~308.15 K下,均四甲苯在所选的9种纯溶剂中的溶解度随温度的增加而增大,且在一定的温度下,均四甲苯在不同溶剂中的溶解度大小顺序为:乙酸异戊酯 > 乙酸正丁酯 > 乙酸乙酯 > 丙酮 > 正丁醇 > 异丙醇 > 乙腈> 乙醇 > 甲醇。
(2) 改进的Apelblat方程、λh方程、NRTL方程及Wilson方程对均四甲苯在9种溶剂中溶解度数据均关联良好,相关系数R2分别不小于0.974、0.960、0.944及0.904;对比4种模型的关联结果,改进的Apelblat方程关联效果最佳,其相关系数R2≥0.974,ARD≤3.47%,且RSMD≤0.22。
(3) 均四甲苯在9种溶剂中的溶解过程为自发的熵增吸热过程。溶解度越大,溶解过程的吉布斯自由能变化越大,熔化焓越大,且体系的混乱度越大。
| [1] |
殷丽娜, 胡永玲, 韩大维. 均四甲苯的制备方法及应用研究[J]. 化学与粘合, 2009, 31(6): 64-68. YIN L N, HU Y L, HAN D W. Preparation and application of durene[J]. Chemistry and Adhesion, 2009, 31(6): 64-68. |
| [2] |
LI M Z, JIAO L K, NAWAZ M A, et al. A one-step synthesis method of durene directly from syngas using integrated catalyst of Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 and Co-Nb/HZSM-5[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2019, 200(8): 103-112. |
| [3] |
任世宇, 陈敏, 李小兵, 等. 雄烯二酮在含大豆油的有机溶剂体系中溶解度的测定与关联[J]. 高校化学工程学报, 2018, 32(3): 507-513. REN S Y, CHEN M, LI X B, et al. Determination and correlation of androstenedione solubility in organic solvents containing soybean-oil[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Chinese Universities, 2018, 32(3): 507-513. |
| [4] |
ZHU A F, HONG K, ZHU F X, et al. Solubility, model correlation, and solvent effect of 2-amino-3-methylbenzoic acid in 12 pure solvents[J]. Journal of Chemical and Engineering Data, 2019, 64(4): 1713-1724. DOI:10.1021/acs.jced.8b01226 |
| [5] |
FAN B J, LI Q S, LU M Y, et al. Measurement and correlation of solubility of 3-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid in ten pure and binary mixed organic solvents from T = (293.15 to 333.15 K)[J]. Journal of Chemical and Engineering Data, 2018, 63(12): 4459-4467. |
| [6] |
LI J, ZENG Z X, SUN L, et al. Solid-liquid phase equilibrium of trans-cinnamic acid in several alcohols: measurements and thermo dynamic modeling[J]. Journal of Chemical and Engineering Data, 2016, 61(3): 1192-1198. DOI:10.1021/acs.jced.5b00814 |
| [7] |
沈乐, 李惠萍, 高江涛, 等. 1-苄基-4-羟甲基-1H-1, 2, 3-三氮唑溶解度的测定及关联[J]. 高校化学工程学报, 2016, 30(1): 1-6. SHEN L, LI H P, GAO J T, et al. Measurement and correlation of 1-benzyl-4-hydroxymethyl-1H-1, 2, 3-triazole solubility[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Chinese Universities, 2016, 30(1): 1-6. |
| [8] |
NONG W J, CHEN X P, WANG L L, et al. Measurement and correlation of solubility of abietic acid in ethanol + water mixtures[J]. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 2014, 68(2): 199-204. |
| [9] |
APELBLAT A, MANZUROLA E. Solubilities of o-acetylsalicylic, 4-aminosalicylic, 3, 5-dinitrosalicylic, and p-toluic acid, and magnesium DL-aspartate in water from T = (278 to 348) K[J]. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 1999, 31(1): 85-91. DOI:10.1006/jcht.1998.0424 |
| [10] |
BUCHOWSKI H, KSIAZCZAK A, PIETRZYK S. Solvent activity along a saturation line and solubility of hydrogen-bonding solids[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1980, 84(9): 975-979. DOI:10.1021/j100446a008 |
| [11] |
WILSON G M. Vapor-liquid equilibrium. XI. a new expression for the excess free energy of mixing[J]. Journal of America Chemistry Society, 1964, 86(2): 127-130. DOI:10.1021/ja01056a002 |
| [12] |
RENON H, PRAUSNITZ J M. Estimation of parameters for the NRTL equation for excess Gibbs energies of strongly nonideal liquid mixtures[J]. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Process Design and Development, 1969, 8(3): 413-419. DOI:10.1021/i260031a019 |
| [13] |
KRIVANKOVA I, MARCISINOVA M, SOHNEL O. Solubility of itaconic and kojic acids[J]. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 1992, 37(1): 23-24. |
| [14] |
瓦拉斯.化工相平衡[M].韩世钧, 译.北京: 中国石化出版社, 1991. STANLEY M W. Phase equilibria in chemical engineering [M]. HAN S J, trans. Beijing: China Petrochemical Press, 1991. |
| [15] |
PRAUSNITZ J M, LICHTENTHALER R N, Azevedo E G. Molecular thermodynamics of fluid-phase equilibria[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2006.
|
| [16] |
WU K, LI Y J. Solid-liquid equilibrium of azacyclotridecan-2-one in 15 pure solvents from T = 273.15 to 323.15 K: Experimental determination and thermodynamic modeling[J]. Journal of Chemical and Engineering Data, 2019, 64(4): 1640-1649. DOI:10.1021/acs.jced.8b01193 |
| [17] |
SUNSANDEE N, SUREN S, LEEPIPATPIBOON N, et al. Determination and modeling of aqueous solubility of 4-position substituted benzoic acid compounds in a high-temperature solution[J]. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 2013, 338(1): 217-223. |
| [18] |
WEI D, PEI Y. Solubility of diphenyl carbonate in pure alcohols from (283 to 333) K[J]. Journal of Chemical and Engineering Data, 2008, 53(11): 2710-2711. DOI:10.1021/je800569v |
| [19] |
ZHANG Y, GUO F, CUI Q, et al. Measurement and correlation of the solubility of vanillic acid in eight pure and water plus ethanol mixed solvents at temperatures from (293.15 to 323.15) K[J]. Journal of Chemical and Engineering Data, 2016, 61(1): 420-429. DOI:10.1021/acs.jced.5b00619 |
| [20] |
CHEN J J, HE J J, LI N X, et al. Determination and correlation of solubility of borneol, camphor, and isoborneol in different solvents[J]. Journal of Chemical and Engineering Data, 2019, 64(4): 1826-1833. |
| [21] |
ZHENG M, CHEN J, CHEN G Q, et al. Solubility modeling and solvent effects of allopurinol in 15 neat solvents[J]. Journal of Chemical and Engineering Data, 2018, 63(10): 3551-3558. |
| [22] |
金克新, 魏东炜, 李洪勋. 四甲苯物系固液平衡测定[J]. 天津大学学报(自然科学与工程技术版), 1991, 24(4): 62-69. JIN K X, WEI D W, LI H X. Sold-liquid equilibria of the isomers of tetramethyl benzene[J]. Journal of Tianjin University (Science and Technology), 1991, 24(4): 62-69. |
| [23] |
KONDEPUDI D K. Introduction to modern thermodynamics[M]. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons Ltd, 2008.
|
| [24] |
SMITH J M, NESS H C V, ABBOTT M M. Introduction to chemical engineering thermodynamics[M]. 7th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2001.
|




